In the modern era of technology, the fusion of satellite data and gardening practices has opened up new avenues for cultivating smart gardens. By harnessing spy satellite data, DIY enthusiasts can transform their gardens into highly efficient, self-regulating ecosystems. This guide will walk you through the process of building a DIY smart garden, leveraging the power of satellite data to enhance plant growth and sustainability.
## Step 1: Research and Planning

Before diving into the project, it’s crucial to do thorough research and planning. Understand the basics of satellite data, its applications in agriculture, and how it can be utilized in gardening. Consider the following points:
– **Identify Garden Goals**: Determine what you want to achieve with your smart garden. This could include maximizing yield, minimizing water usage, or creating a sustainable ecosystem.
– **Select Plants**: Choose plants that are well-suited to the local climate and soil conditions. Research which plants are compatible with the use of satellite data.
– **Gather Tools and Materials**: List all the necessary tools and materials, including a satellite data subscription, sensors, and garden equipment.
## Step 2: Accessing Spy Satellite Data
To build a smart garden, you will need access to satellite data. Here’s how to get started:
– **Subscription**: Sign up for a satellite data provider that offers agricultural services. Companies like Airbus Defence and Space, Maxar Technologies, and DigitalGlobe provide access to high-resolution satellite imagery and data.
– **Data Processing**: Once you have the data, process it to extract relevant information, such as soil composition, weather patterns, and plant health indicators.
– **Integrate Data**: Use satellite imagery and data to create a digital map of your garden, which will help you make informed decisions about planting, watering, and fertilizing.
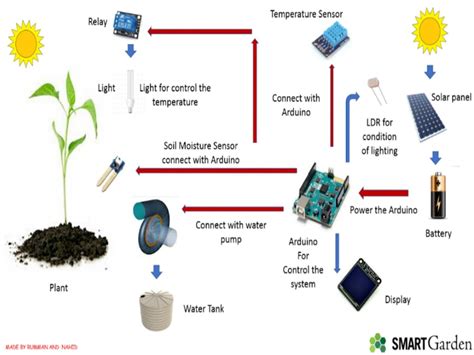
## Step 3: Installing Garden Sensors
To further enhance the intelligence of your smart garden, install various sensors to gather real-time data:
– **Weather Stations**: Monitor temperature, humidity, rainfall, and wind speed to optimize irrigation and protect your plants from adverse conditions.
– **Soil Moisture Sensors**: Track soil moisture levels to ensure plants receive the right amount of water.
– **Light Sensors**: Measure light intensity to adjust shading or artificial lighting for optimal plant growth.
## Step 4: Setting Up Automation Systems
Automation is key to a smart garden. Here’s how to set up your automation systems:
– **Irrigation System**: Use soil moisture sensors to trigger irrigation systems, ensuring that plants receive the precise amount of water needed.
– **Lighting Control**: Integrate light sensors to adjust artificial lighting for plants that require specific light conditions.
– **Fertilization System**: Use satellite data and soil sensors to determine the right time and amount of fertilizer to apply.
## Step 5: Monitoring and Maintenance
Once your DIY smart garden is up and running, it’s important to monitor and maintain it regularly:
– **Data Analysis**: Regularly review satellite data, sensor readings, and garden performance to identify areas for improvement.
– **Adjustment**: Make necessary adjustments to irrigation, lighting, and fertilization schedules based on the data and observations.
– **Maintenance**: Keep sensors and equipment clean and functioning properly to ensure accurate data collection.
## Conclusion
Building a DIY smart garden using spy satellite data can revolutionize your gardening experience. By leveraging technology and data, you can create a more efficient, sustainable, and productive garden. With careful planning and ongoing maintenance, your smart garden will reward you with lush, healthy plants and a deeper understanding of the intricate balance of nature.