In the heart of Silicon Valley, a new breed of activists is emerging, fighting for the principle of “Right-to-Repair.” These “Right-to-Repair” hacktivists are taking a stand against the restrictive practices of major tech companies, advocating for the freedom to repair and modify consumer electronics.
The movement gained momentum as tech giants like Apple, Samsung, and Google have been accused of designing products that are intentionally difficult to repair. This has led to skyrocketing repair costs and a reliance on the manufacturers for any maintenance or upgrades. The “Right-to-Repair” activists argue that this practice is not only unfair to consumers but also environmentally unsustainable.

At the forefront of this movement are tech-savvy individuals who are using their skills to expose the limitations imposed by manufacturers. These hacktivists are leveraging the power of social media, online forums, and DIY repair communities to spread awareness and mobilize support.
One of the key strategies employed by these activists is the creation of open-source repair guides. By providing detailed instructions on how to disassemble and repair various devices, they are empowering consumers to take control of their own electronics. This not only saves money but also fosters a sense of ownership and satisfaction.
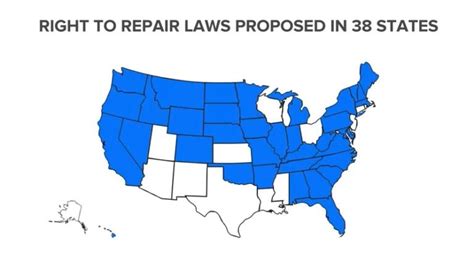
Moreover, the “Right-to-Repair” hacktivists are targeting legislation to ensure that consumers have the right to repair their own devices. They are pushing for the implementation of “Right-to-Repair” laws that would require manufacturers to provide access to repair information, tools, and parts.
The success of this movement can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the increasing awareness of environmental issues has led many consumers to question the sustainability of the current “throwaway” culture. Secondly, the growing cost of repairs has prompted many to seek alternative solutions. Lastly, the availability of online resources and communities has made it easier for individuals to collaborate and share knowledge.
Despite facing resistance from tech companies, the “Right-to-Repair” hacktivists in Silicon Valley are determined to make a lasting impact. They believe that the right to repair is a fundamental consumer right that should be protected.
As the movement gains traction, it is likely that more consumers will join the fight for “Right-to-Repair.” This could lead to significant changes in the way manufacturers design and produce their products, ultimately benefiting both consumers and the environment.
In conclusion, the rise of “Right-to-Repair” hacktivists in Silicon Valley is a testament to the power of technology and the collective will of individuals to challenge the status quo. As they continue to advocate for consumer rights and environmental sustainability, the future of repair may look very different from what we know today.