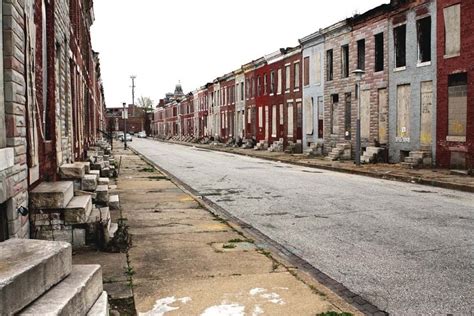
In recent years, the term “climate ghettos” has emerged to describe the growing trend of isolated, environmentally vulnerable communities that are predominantly located in abandoned suburbs. These neighborhoods, once bustling with activity, have now fallen into disrepair, leaving residents to face the brunt of climate change with limited resources and support. This article delves into the causes and consequences of the rise of climate ghettos in abandoned suburbs.
The decline of abandoned suburbs can be attributed to a variety of factors, including economic restructuring, suburban sprawl, and the rise of urban living. As cities expand, many suburban neighborhoods struggle to maintain their appeal, leading to population loss and a decline in property values. This process is exacerbated by climate change, which creates a cycle of abandonment and vulnerability.

One of the primary reasons for the rise of climate ghettos is the lack of infrastructure investment in these communities. Many abandoned suburbs were built in the mid-20th century with little consideration for sustainability or resilience. As a result, they are ill-equipped to handle the challenges posed by climate change, such as extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and air pollution.
Moreover, climate ghettos are often characterized by socio-economic disadvantage. Residents in these neighborhoods tend to be lower-income, with limited access to resources such as healthcare, education, and transportation. This vulnerability is compounded by the fact that climate change disproportionately affects marginalized communities, exacerbating existing inequalities.
The consequences of living in a climate ghetto are profound. Residents are more likely to suffer from health issues related to air pollution, such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. They also face increased risks of displacement due to flooding and other climate-related events. Additionally, the lack of infrastructure and community support makes it difficult for residents to adapt to the changing climate.
In response to the growing threat of climate ghettos, policymakers and community leaders must take action to address the root causes of this issue. This includes investing in sustainable infrastructure, such as green roofs, rain gardens, and resilient buildings, to mitigate the impacts of climate change. It also involves implementing policies that promote equitable access to resources and services.
Furthermore, community engagement is crucial in the fight against climate ghettos. By empowering residents to take an active role in their neighborhoods, we can foster a sense of ownership and resilience. This can be achieved through programs that encourage community-driven initiatives, such as urban gardening, renewable energy projects, and climate education.
The rise of climate ghettos in abandoned suburbs is a wake-up call to the urgent need for climate justice. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, it is imperative that we prioritize the needs of vulnerable communities, ensuring that no one is left behind. By investing in sustainable infrastructure, promoting equitable access to resources, and fostering community engagement, we can work towards a more resilient and just future for all.